TIL 날짜
2023.12.08
Contents
- 의미
- 배열과 연결 리스트의 차이점
- 연결 리스트 메소드 활용방법 (1)
연결 리스트
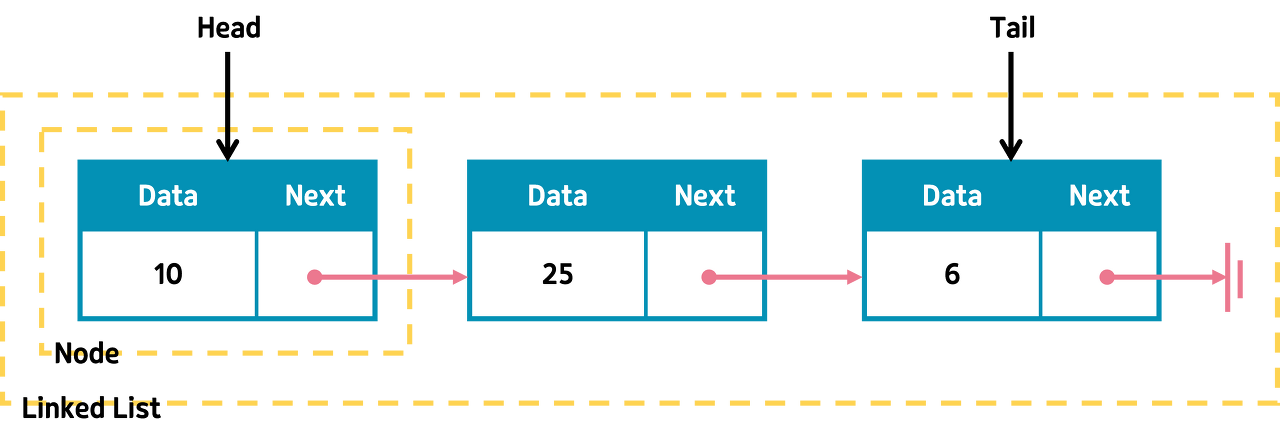
의미: 하나의 개체를 이루는 노드가 연결되어 리스트를 이루는 구조
구조
- 데이터: 각 노드가 실제로 저장하는 데이터, 연결 리스트가 저장하는 정보나 값
- 포인터(링크): 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터, 이 링크를 통해 순서대로 노드들이 연결되어 있다.
- 헤드(head): 맨 앞의 노드
- 테일(tail): 맨 마지막 노드
배열과 연결 리스트의 차이점
배열
메모리 할당 방식
- 연속된 메모리 공간에 데이터를 저장한다.
크기 조절 및 삽입/삭제 연산
- 크기가 고정되어 있어 삽입 및 삭제 연산이 어렵고 비용이 높을 수 있다
접근 속도
- 인덱스를 통한 빠른 임의 접근이 가능하며 특정 요소에 대한 접근이 가능하다.
메모리 사용
- 크기가 고정되어 있기 때문에 미리 할당된 공간 외에는 추가적인 메모리를 사용하지 않는다
연결 리스트
메모리 할당 방식
- 각 노드가 독립적으로 메모리에 할당되며 이들은 포인터를 통해 서로 연결되어 있다.
크기 조절 및 삽입/삭제 연산
- 동적으로 크기를 조절할 수 있으며, 특히 중간에 노드를 추가하거나 삭제하는 연산이 배열에 비해 효율적이다.
접근 속도
- 노드를 순회하기 때문에 배열에 비해 느리며 특정 요소에 대한 접근이 불가능하다.
메모리 사용
- 포인터로 연결되어 있기에 메모리 사용이 좀 더 유연하지만 추가적인 포인터를 사용하여 메모리 소비가 생길 수 있다.
연결 리스트 메소드 활용방법 (1)
기본적인 툴
class Node{
constructor(val){
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
class SinglyLinkedList{
constructor(){
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}}
1. push()
class SinglyLinkedList{
push(val){
let newNode = new Node(val);
if(!this.head){
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = this.head;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length++
return this
}
}
2. pop()
class SinglyLinkedList{
pop(){
if(!this.head) return undefined;
let current = this.head;
let newTail = current;
while(current.next){
newTail = current;
current = current.next;
}
this.tail = newTail;
this.tail.next = null;
this.length--;
if(this.length === 0){
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
return current;
}
}
3. shift()
class SinglyLinkedList{
shift(){
if(!this.head) return undefined
let currentHead = this.head
this.head = currentHead.next;
this.length--;
return currentHead
}
}
4.unshift()
class SinglyLinkedList{
unshift(val){
let newNode = new Node(val);
if(!head){
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = this.head;
}
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
this.length++
return this;
}
}